12.9 Computing pairwise distance
Read in the FASTA file of aligned sequences with the read.dna function from ape:
We then compute the pairwise distance matrix:
We can plot this matrix to visualize it:
# use the "melt_dist" function from harrietr package to convert
# the distance matrix to "long" format for ggplot
D_melted <- rbind(melt_dist(D, order = ids),
melt_dist(t(D), order = rev(ids)))## Warning: `gather_()` was deprecated in tidyr 1.2.0.
## ℹ Please use `gather()` instead.
## ℹ The deprecated feature was likely used in the harrietr package.
## Please report the issue at <https://github.com/andersgs/harrietr/issues>.
## This warning is displayed once every 8 hours.
## Call `lifecycle::last_lifecycle_warnings()` to see where this warning was
## generated.# plot distance matrix
ggplot(data = D_melted) +
geom_tile(aes(x = iso1, y = iso2, fill = (dist + 1e-5))) +
theme_classic() +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 90, hjust = 1)) +
scale_fill_viridis_c(name = "distance") +
xlab("sample") +
ylab("sample")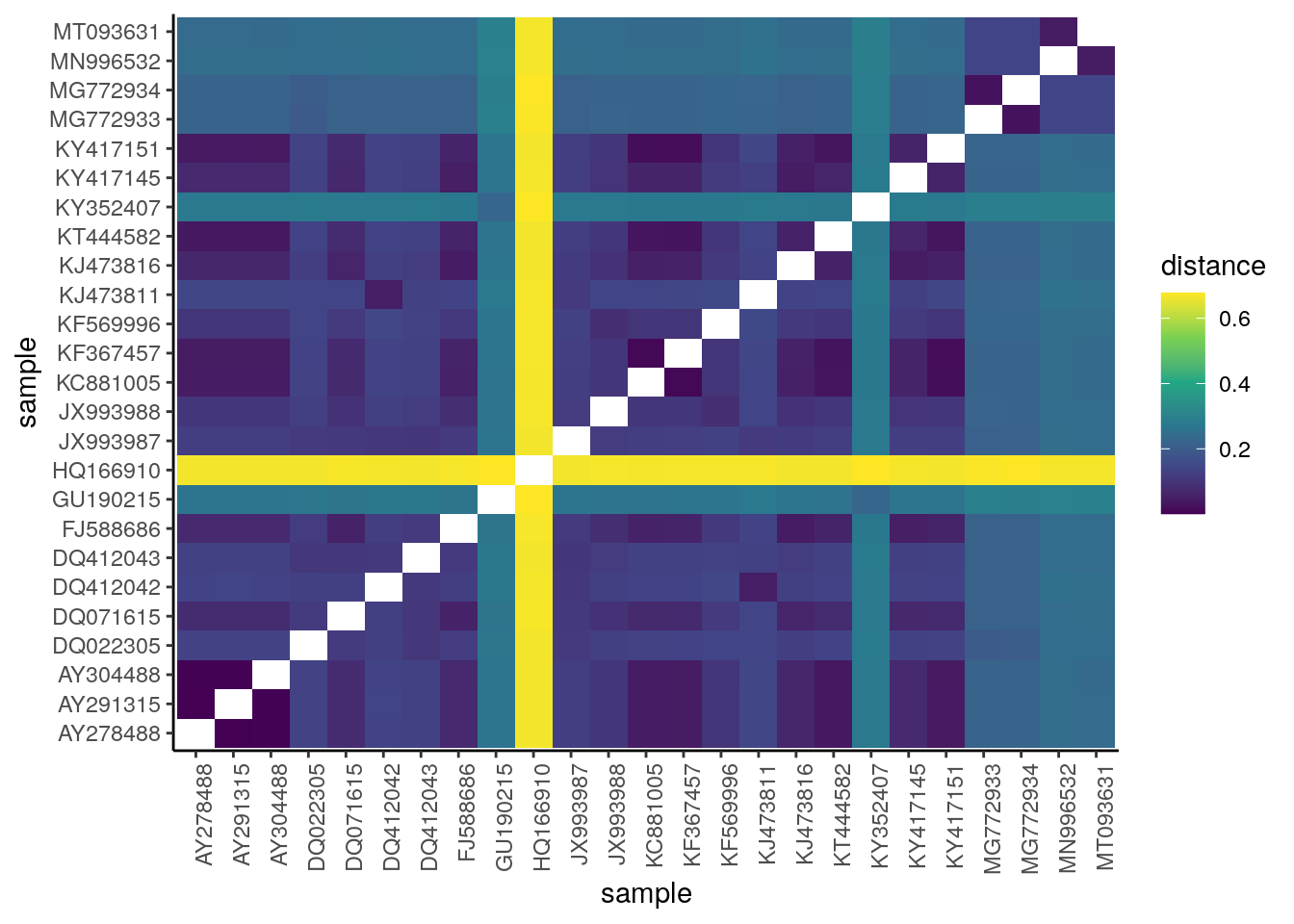
Interpreting the distance matrix
Most of these coronaviruses seem to be fairly similar – i.e., there’s no clear clustering of sequences – besides HQ166910, which looks genetically distinct from the other sequences.