12.5 SARS-CoV-2 mutation landscape
The phylogeny page also has a “diversity” section, where it plots the number of mutations observed in different regions of the SARS-CoV-2 genome sequence.
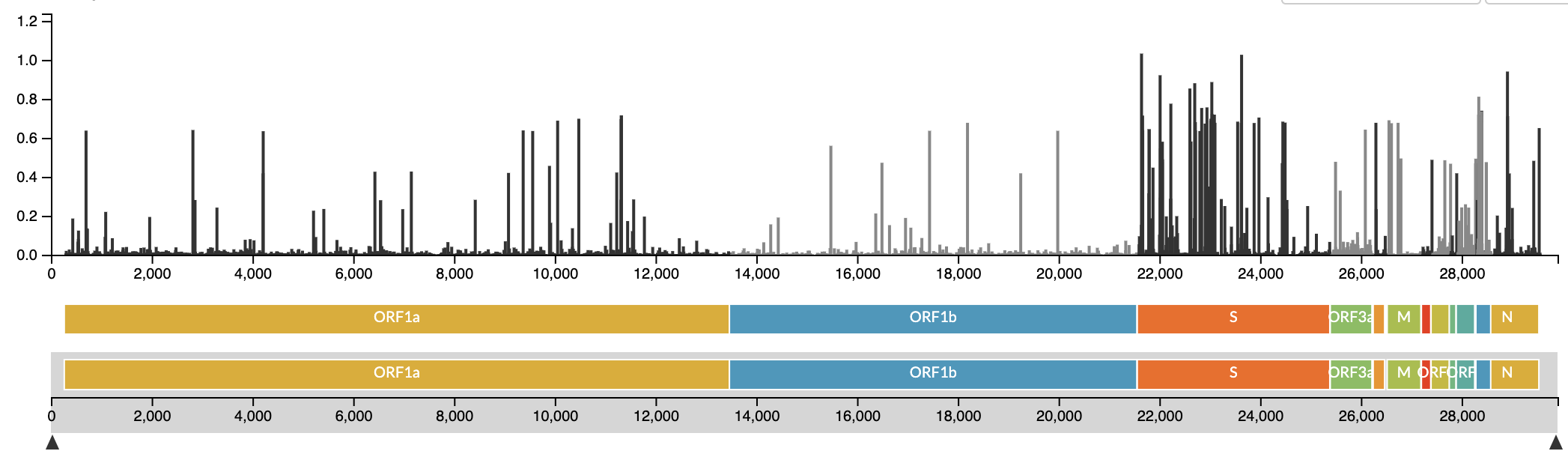
Fig. 4. Genomic distribution of mutations across SARS-CoV-2 strains (source).
Does this plot imply that specific regions of the SARS-CoV-2 genome are more susceptible to mutation?
No – this plot can be interpreted as showing where mutations persist in the SARS-CoV-2 genome, not where they occur.
Although mutation occurrence is mostly random, the genomic distribution we see in this plot has been filtered by natural selection. Beneficial mutations are selected for, causing them to appear more frequently in pathogenically important regions like the spike protein (S).
We sometimes see recurring independent mutations where the same amino acid is changed across different SARS-CoV-2 strains, which is extremely strong evidence of selection.