11.7 Splicing QTLs
In addition to variants that impact gene expression, there are splicing quantitative trait loci (sQTLs) that alter how a gene is spliced. Some sQTL mechanisms include:
- Create or destroying a splicing donor/acceptor site
- Changing the binding site for a protein that regulates splicing
- Altering a splicing factor protein itself
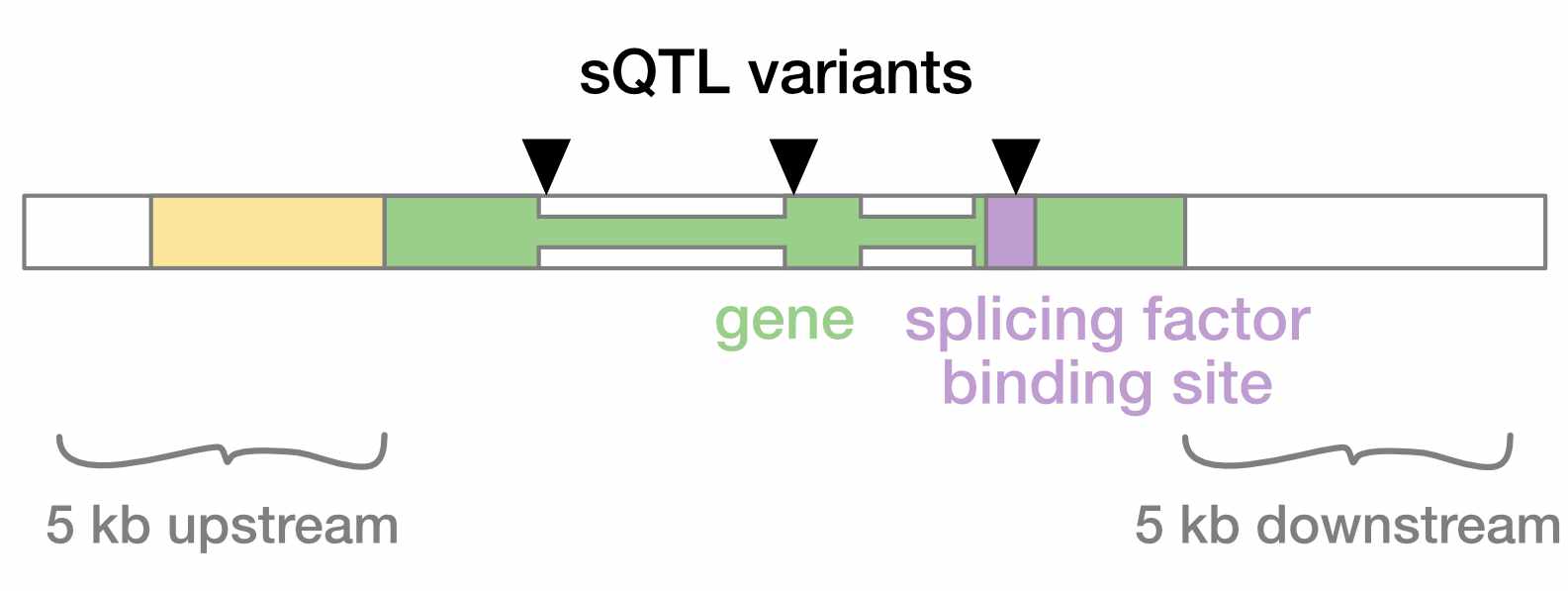
Fig. 7. sQTLs may alter splice donor/acceptor sites, or binding sites for transcription factors that regulate splicing.
sQTLs in GTEx
The GTEx Portal also provides a list of sQTLs for each gene. Note that the violin plots for these QTLs refer to a specific intron of DNMT3A whose inclusion rate is affected by each SNP.
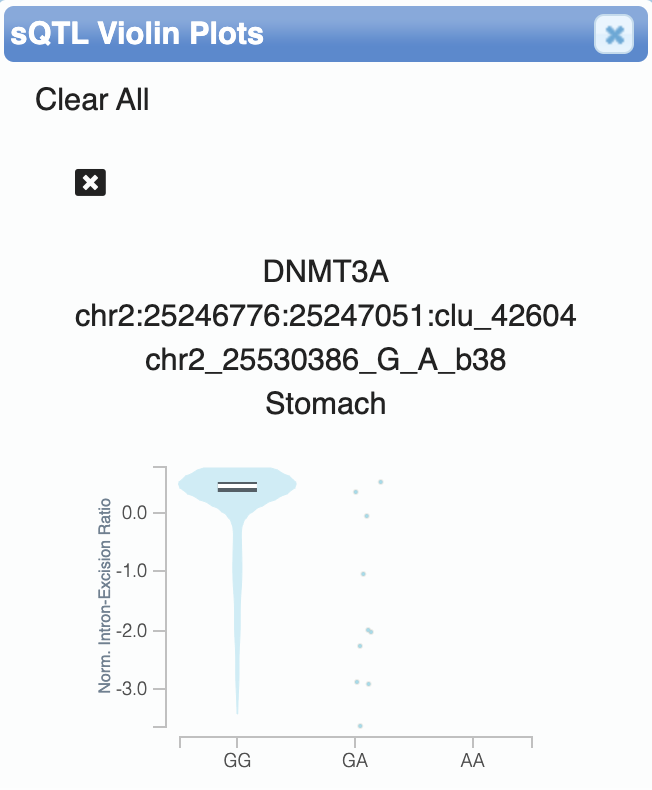
Fig. 8. The
A allele at the chr2_25530386_G_A_b38 SNP reduces excision of the chr2:25246776:25247051:clu_42604 intron of DNMT3A.