2.1 DNA sequencing data
These days, the vast majority of genomic data is generated through high-throughput Illumina short-read sequencing. The broad steps of this sequencing process are:
- Extract DNA
- Fragment DNA
- Prepare for sequencer (add adapters, etc.)
- Amplify DNA
- Sequencing (add fluorescently labeled nucleotides that are read by a digital camera)
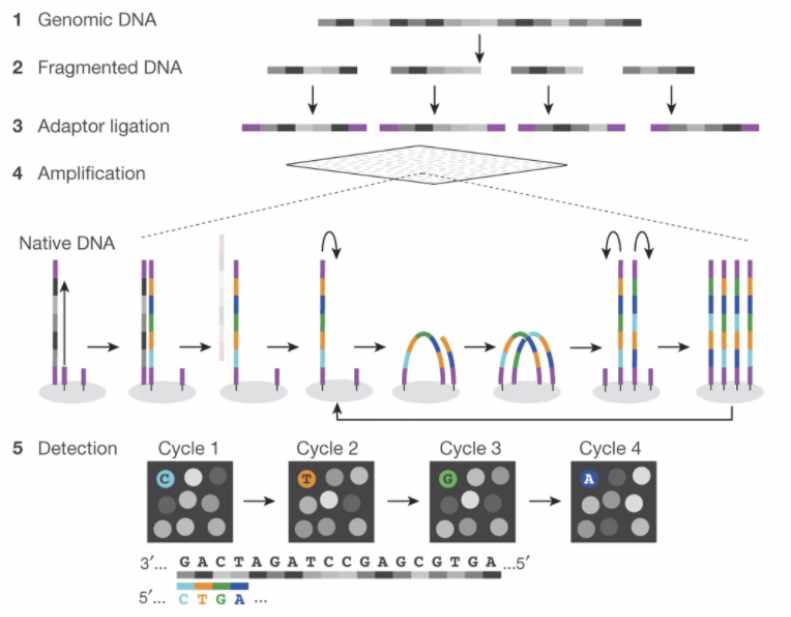
Fig. 1 (source). Schematic of Illumina short-read sequencing.
This sequencing approach is fast and cost efficient, but introduces two main limitations.
- Because of the fragmentation step, the resulting sequencing reads are extremely short (~150 bp).
- We don’t know where in the genome the sequencing reads came from. (This is a limitation common to nearly every sequencing experiment.)